Login [Mobile]
Simple mobile reversing challenge (that doesn’t require much mobile knowledge XD). First mobile challenge from DSO-NUS 2021.
Problem Statement
It's time for a simple, relaxing challenge.
Can you find the correct credentials?
Files (Any of the links are fine):
https://nusdsoctf2.s3-ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/S3/Login/login.apk
https://nusdsoctf.s3-ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/S3/Login/login.apk
>> This challenge unlocks another challenge
>> Flag format conversion may have to be done for this challenge (Refer to notifications)
Solution
We can use the script d2j-dex2jar in dex-tools to turn the apk file to a jar file, then using JD-GUI to decompile the jar file, we can try and find some interesting functions.
Eventually, I found myself to /com/ctf.level1/data/LoginDataSource.class, which has a function called login, and it mentions the word ‘flag’. So let’s understand what the code is trying to do:
public Result<LoggedInUser> login(String paramString1, String paramString2) {
...
paramString1 = paramString2.substring(0, 4);
if (!paramString1.equals(getJavaPassword())) {
Log.d(this.TAG, "Wrong password");
return new Result.Error(new Exception("wrong credentials"));
}
String str = paramString2.substring(4);
if (!str.equals(getNativePassword())) {
Log.d(this.TAG, "Wrong password!");
return new Result.Error(new Exception("wrong credentials"));
}
try {
MessageDigest messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
StringBuilder stringBuilder2 = new StringBuilder();
this();
messageDigest.update(stringBuilder2.append(paramString1).append(str).toString().getBytes());
byte[] arrayOfByte = messageDigest.digest();
String str1 = this.TAG;
StringBuilder stringBuilder1 = new StringBuilder();
this();
Log.d(str1, stringBuilder1.append("The flag is ").append(toHex(arrayOfByte)).toString());
...
}
Reading the code that reveals the flag, it seems that we pass in the character bytes of the string paramString2 (which is the password) into SHA256. The password is checked at the two if statements of this method.
The first one checks the first four characters against getJavaPassword(), if we look at that function:
private String m_password = "7470CB2F2412053D0A3CEC3D07CAE4A4";
...
public String getJavaPassword() {
String str;
try {
str = AESTools.decrypt(this.m_password);
} catch (Exception exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
str = "";
}
return str;
}
// Inside AESTools.class
private static final byte[] keyValue = "!@#$%^&*()_+abcd".getBytes();
...
public static String decrypt(String paramString) throws Exception {
return new String(decrypt(toByte(paramString)));
}
private static byte[] decrypt(byte[] paramArrayOfbyte) throws Exception {
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(keyValue, "AES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES");
cipher.init(2, secretKeySpec);
return cipher.doFinal(paramArrayOfbyte);
}
...
public static byte[] toByte(String paramString) {
int i = paramString.length() / 2;
byte[] arrayOfByte = new byte[i];
for (byte b = 0; b < i; b++) {
int j = b * 2;
arrayOfByte[b] = Integer.valueOf(paramString.substring(j, j + 2), 16).byteValue();
}
return arrayOfByte;
}
We can do some useful googling for the Java’s specification for the Cipher class to understand what this all does. In short, getJavaPassword() returns the AES decrypted string of the hex string m_password with the key keyValue.
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
keyValue = b"!@#$%^&*()_+abcd"
tmp = "7470CB2F2412053D0A3CEC3D07CAE4A4"
m_password = []
for i in range(0, len(tmp), 2):
m_password.append(int(tmp[i:i+2], 16))
m_password = bytes(m_password)
cipher = AES.new(keyValue, AES.MODE_ECB)
first_4 = cipher.decrypt(m_password)[:4]
Then we need to find the rest of the password, it checks against the value of a native method getNativePassword(). To do this, we first unzip or run apktool on the apk file, and throw the binary in /lib/x86 into ghidra.
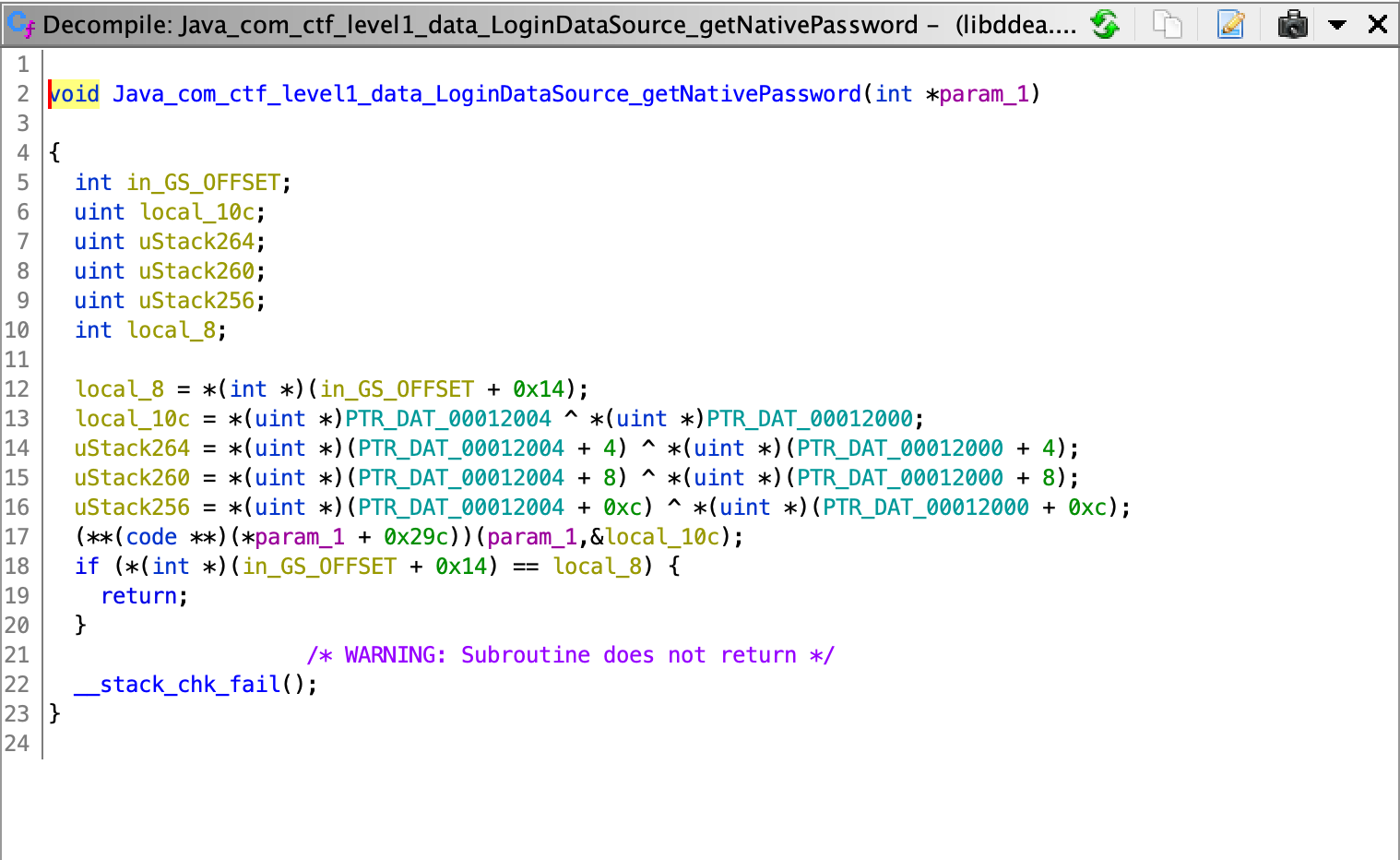
So it’s just simple xor between two byte sequences at addresses 0x010674 and 0x010685, and judging from the indices, it should be of length 16 (4 bytes done 4 times).
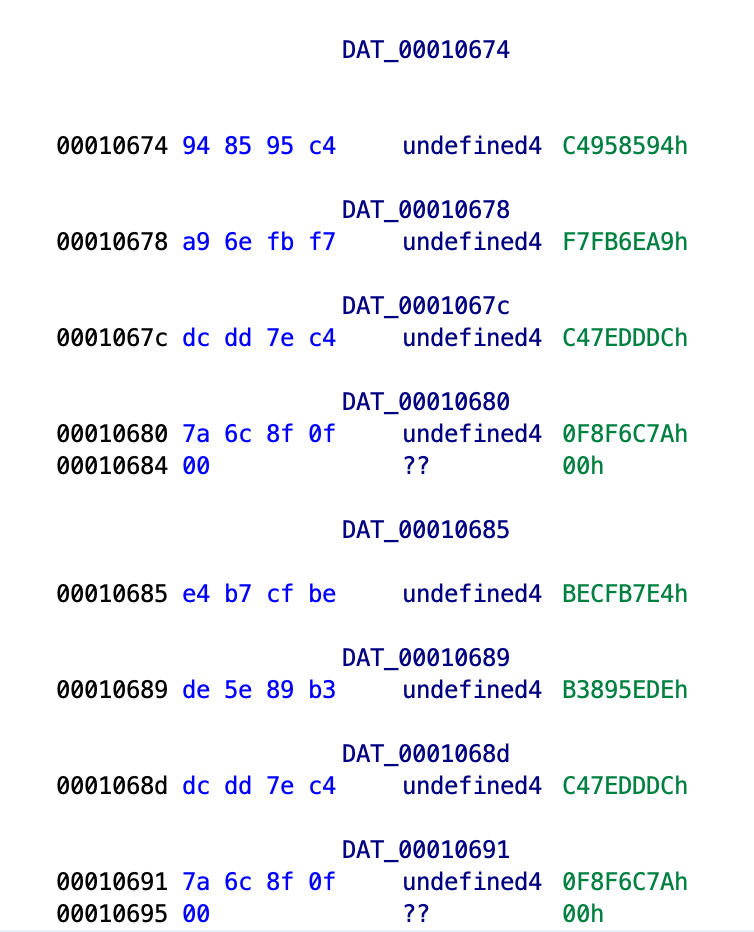
Finally, we can put together the first part and this xor part.
Final Script
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
keyValue = b"!@#$%^&*()_+abcd"
tmp = "7470CB2F2412053D0A3CEC3D07CAE4A4"
m_password = []
for i in range(0, len(tmp), 2):
m_password.append(int(tmp[i:i+2], 16))
m_password = bytes(m_password)
cipher = AES.new(keyValue, AES.MODE_ECB)
first_4 = cipher.decrypt(m_password)[:4]
# can exclude the last 8 bytes since they are the same
a = [0x94, 0x85, 0x95, 0xc4, 0xa9, 0x6e, 0xfb, 0xf7, 0xdc, 0xdd, 0x7e, 0xc4, 0x7a, 0x6c, 0x8f, 0x0f]
b = [0xe4, 0xb7, 0xcf, 0xbe, 0xde, 0x5e, 0x89, 0xb3, 0xdc, 0xdd, 0x7e, 0xc4, 0x7a, 0x6c, 0x8f, 0x0f]
the_rest = b""
for i in range(len(a)):
the_rest += bytes([a[i] ^ b[i]])
print(first_4 + the_rest)
Output
b'L1v3p2Zzw0rD\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00'
Finally, we put L1v3p2Zzw0rD into SHA256.
Flag: DSO-NUS{71bcade1b51d529ad5c9d23657662901a4be6eb7296c76fecee1e892a2d8af3e}
